In the dynamic world of options trading, the “Straddle Strategy” stands out as a powerful tool that allows investors to capitalize on market movements without having to predict the direction of the underlying asset’s price. The straddle strategy is particularly useful in volatile market conditions, where sharp price swings can create significant opportunities for profit. In this blog post, we will delve into the intricacies of the straddle strategy, understanding how it works, when to use it, and its potential benefits and risks.
1. What is the Straddle Strategy?
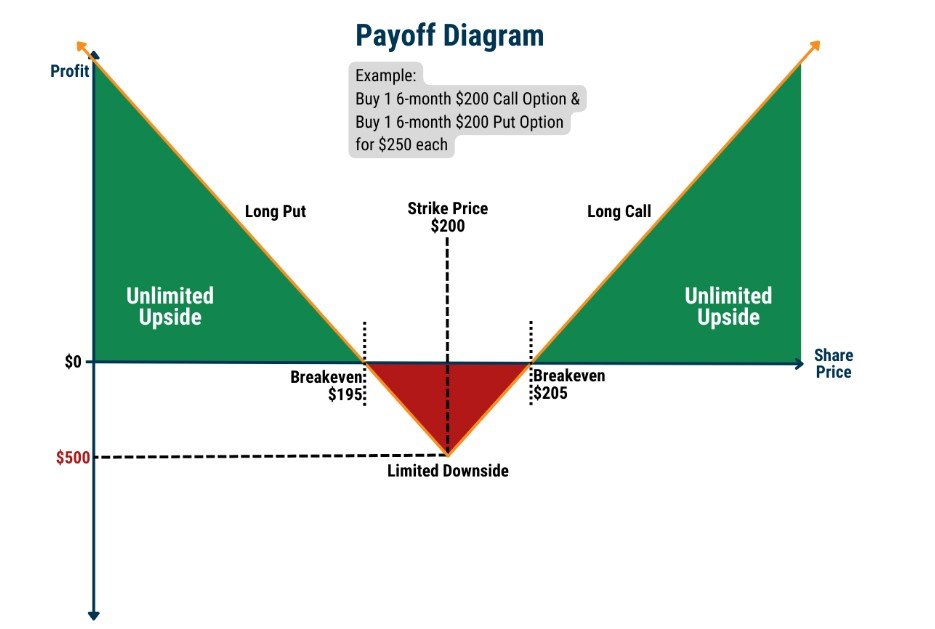
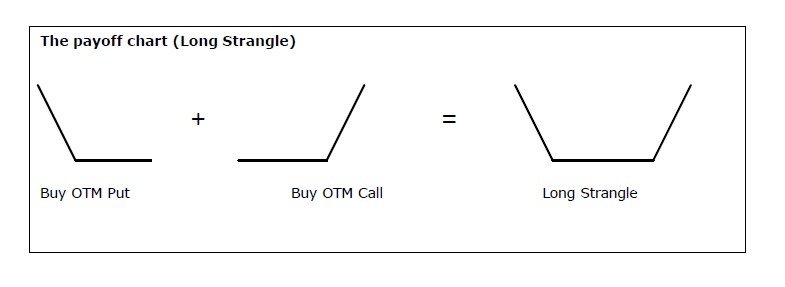
A straddle is an options strategy that involves simultaneously purchasing a call option and a put option on the same underlying asset, with the same strike price and expiration date. Essentially, the straddle strategy allows traders to take a position on both sides of the market, betting on an imminent significant price movement in either direction.
2. How Does the Straddle Strategy Work?
The straddle strategy thrives on market volatility. When a trader implements a straddle, they are anticipating a major price swing, but they are uncertain about the direction in which the price will move. By combining a call and put option, the trader creates a potential profit zone that encompasses both upward and downward price movements.
- Scenario 1 – Market Rises: If the underlying asset’s price rises significantly above the strike price, the call option will be “in-the-money” and generate a profit, while the put option will expire “out-of-the-money,” resulting in a limited loss due to the premium paid for the put.
- Scenario 2 – Market Declines: Conversely, if the underlying asset’s price drops significantly below the strike price, the put option will be “in-the-money” and produce a profit, while the call option will expire “out-of-the-money,” resulting in a limited loss due to the premium paid for the call.
3. When to Use the Straddle Strategy?
The straddle strategy is most effective in situations where a significant market event or news is expected to trigger substantial price movements. Some common scenarios where traders may employ the straddle strategy include:
- Earnings Announcements: Companies often experience significant stock price movements after releasing their earnings reports. Traders can use the straddle strategy to profit from potential large price swings following these announcements.
- Merger and Acquisition News: When companies announce mergers or acquisitions, their stock prices can experience sharp fluctuations. Traders may utilize the straddle strategy to benefit from such events.
- Product Launches or Regulatory Decisions: For companies in sectors prone to regulatory decisions or product launches (e.g., pharmaceuticals), traders may employ the straddle strategy to capitalize on potential market reactions.
4. Benefits of the Straddle Strategy:
- Limited Risk: The maximum loss for a straddle is limited to the combined premiums paid for both the call and put options.
- Potential for Significant Profit: If the underlying asset experiences a substantial price movement in either direction, the profit potential can be substantial.
- Hedging Against Volatility: The straddle strategy can be used as a form of volatility hedge, especially during uncertain market conditions.
5. Risks of the Straddle Strategy:
- Time Decay: As with any options strategy, time decay can erode the value of both the call and put options, leading to losses if the underlying asset’s price does not move significantly.
- Lack of Price Movement: If the underlying asset’s price remains relatively stable, the combined premiums paid for the options may result in a loss.
Sure! Let’s illustrate the straddle strategy with a hypothetical example:
Example: Trading ABC Inc. Straddle
Step 1: Identifying the Opportunity
Suppose you are an options trader closely monitoring ABC Inc., a technology company known for its quarterly earnings volatility. The company is set to release its quarterly earnings report, and you expect a significant price movement in either direction due to the earnings announcement.
Step 2: Setting Up the Straddle
Before the earnings announcement, you decide to implement the straddle strategy on ABC Inc. You purchase both a call option and a put option with the following details:
- Current ABC Inc. Stock Price: $100
- Strike Price of Both Options: $100
- Expiration Date: Next month
- Call Option Premium: $5
- Put Option Premium: $4
Step 3: Analyzing Outcomes
There are three possible scenarios after the earnings announcement:
Scenario 1: Positive Earnings Surprise (Bullish Move)
After the earnings announcement, ABC Inc. delivers impressive results, and the stock price soars to $120.
Result:
- The call option is now “in-the-money” with a profit of $20 ($120 stock price – $100 strike price).
- The put option expires “out-of-the-money,” resulting in a loss of $4 (the premium paid for the put).
Total Profit: $20 – $4 = $16
Scenario 2: Negative Earnings Surprise (Bearish Move)
Suppose ABC Inc.’s earnings report disappoints the market, causing the stock price to plummet to $80.
Result:
- The put option is now “in-the-money” with a profit of $20 ($100 strike price – $80 stock price).
- The call option expires “out-of-the-money,” resulting in a loss of $5 (the premium paid for the call).
Total Profit: $20 – $5 = $15
Scenario 3: Limited Price Movement
In this scenario, ABC Inc.’s earnings report is in line with expectations, and the stock price remains relatively stable at $100.
Result:
- Both the call and put options expire “out-of-the-money.”
- The trader incurs a loss of $9 (the combined premiums paid for both options).
Step 4: Evaluating the Outcome
As we can see, the straddle strategy provides the trader with the potential to profit from significant price movements in either direction. In our example, the trader realized a profit in both the bullish and bearish scenarios, while in the limited price movement scenario, they incurred a loss limited to the combined premiums paid.
Conclusion
The straddle strategy is a valuable tool in options trading, allowing traders to benefit from significant price movements without needing to predict the direction of the market. However, it’s essential to be mindful of the potential risks, including time decay and the need for substantial price movement to offset the combined premiums paid.
To successfully implement the straddle strategy, traders should carefully analyze market conditions, implied volatility, and upcoming events that may trigger substantial price swings. With proper risk management and an understanding of market dynamics, the straddle strategy can be a powerful addition to an options trader’s arsenal.
The straddle strategy is a versatile and powerful tool that empowers traders to profit from significant price movements, regardless of the direction. By simultaneously holding both call and put options, traders position themselves to capitalize on volatility and key market events. However, the straddle strategy is not without risks, and traders should carefully assess market conditions, implied volatility, and the potential for significant price swings before employing this strategy.
As with all options trading strategies, proper risk management, and a thorough understanding of market dynamics are essential to successful implementation. Remember, options trading carries inherent risks, and it is crucial to trade with a disciplined approach and only risk capital you can afford to lose.