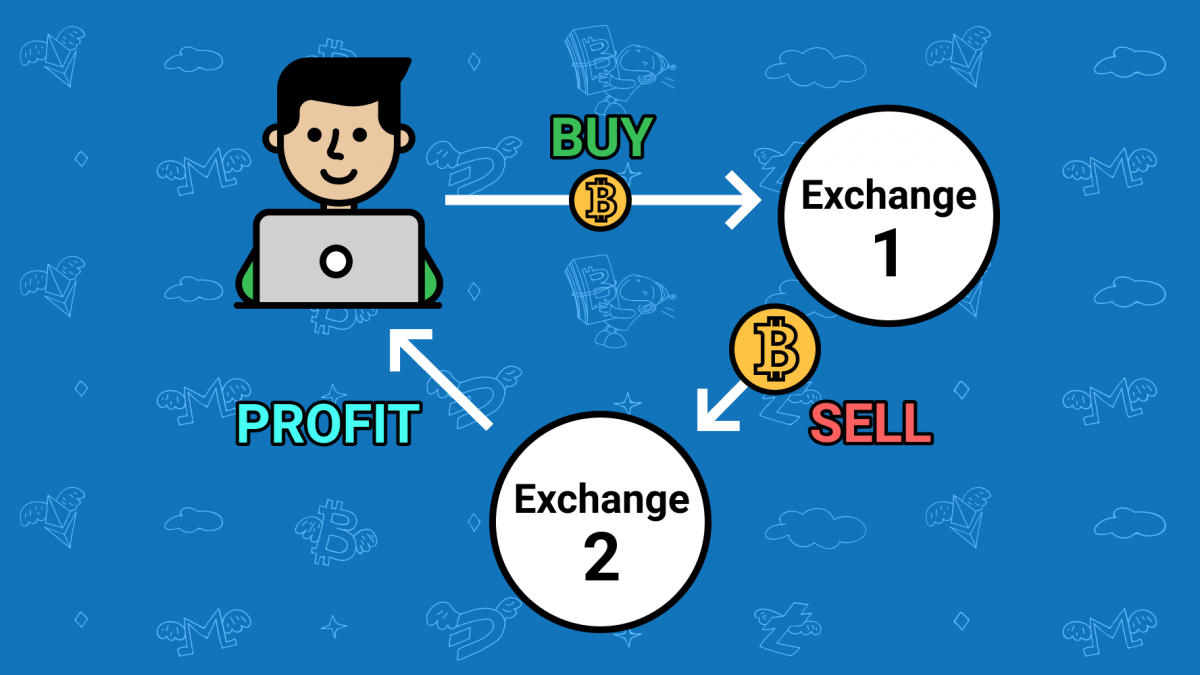
Cross-exchange arbitrage is a trading strategy that capitalizes on temporary price discrepancies for the same cryptocurrency across different cryptocurrency exchanges. This strategy involves buying the cryptocurrency at a lower price on one exchange and simultaneously selling it at a higher price on another exchange, thereby locking in risk-free profits. Cross-exchange arbitrage is particularly prevalent in the cryptocurrency market due to its decentralized nature and varying levels of liquidity on different exchanges. Let’s delve into cross-exchange arbitrage with a detailed example:
Example of Cross-Exchange Arbitrage:
Let’s consider two popular cryptocurrency exchanges, Exchange A and Exchange B. On Exchange A, the current price of Bitcoin (BTC) is $50,000, while on Exchange B, the price of Bitcoin is $50,500. This price difference presents a potential cross-exchange arbitrage opportunity.
Step 1: Identify the Opportunity
The price difference between the two exchanges indicates a potential arbitrage opportunity. The trader can now proceed to execute the arbitrage strategy.
Step 2: Execute the Arbitrage
To execute the cross-exchange arbitrage, the trader will follow these steps:
- Buy Bitcoin on Exchange A: The trader buys Bitcoin at the lower price of $50,000 on Exchange A.
- Transfer Bitcoin to Exchange B: The trader then transfers the Bitcoin purchased on Exchange A to their account on Exchange B. This step involves a blockchain transaction and might incur some fees.
- Sell Bitcoin on Exchange B: On Exchange B, where the Bitcoin price is $50,500, the trader sells the Bitcoin at the higher price.
Step 3: Calculate Profits
The trader has executed the cross-exchange arbitrage and locked in profits. Let’s calculate the profits using a simplified scenario (ignoring transaction fees):
- Buy Price (Exchange A): $50,000
- Sell Price (Exchange B): $50,500
- Amount of Bitcoin Traded: 1 BTC
Profit per Bitcoin = Sell Price – Buy Price = $50,500 – $50,000 = $500
Total Profit = Profit per Bitcoin * Amount of Bitcoin Traded = $500 * 1 BTC = $500
The trader has made a risk-free profit of $500 by exploiting the price discrepancy between the two exchanges.
Notes:
- In reality, cross-exchange arbitrage may involve fees, such as transaction fees, withdrawal fees, and exchange fees, which will impact the overall profit calculation.
- The speed and efficiency of executing cross-exchange arbitrage are crucial, as price discrepancies can disappear rapidly in the fast-paced cryptocurrency market.
Conclusion
Cross-exchange arbitrage is a popular trading strategy in the cryptocurrency market, where price discrepancies can arise due to the decentralized nature of exchanges and variations in liquidity. By buying an asset at a lower price on one exchange and selling it at a higher price on another, traders can exploit these inefficiencies and generate risk-free profits. However, traders must consider transaction fees, execution speed, and market volatility when executing cross-exchange arbitrage. Successful cross-exchange arbitrage requires advanced technology, low-latency access to multiple exchanges, and thorough risk management to navigate the ever-changing landscape of the cryptocurrency market.